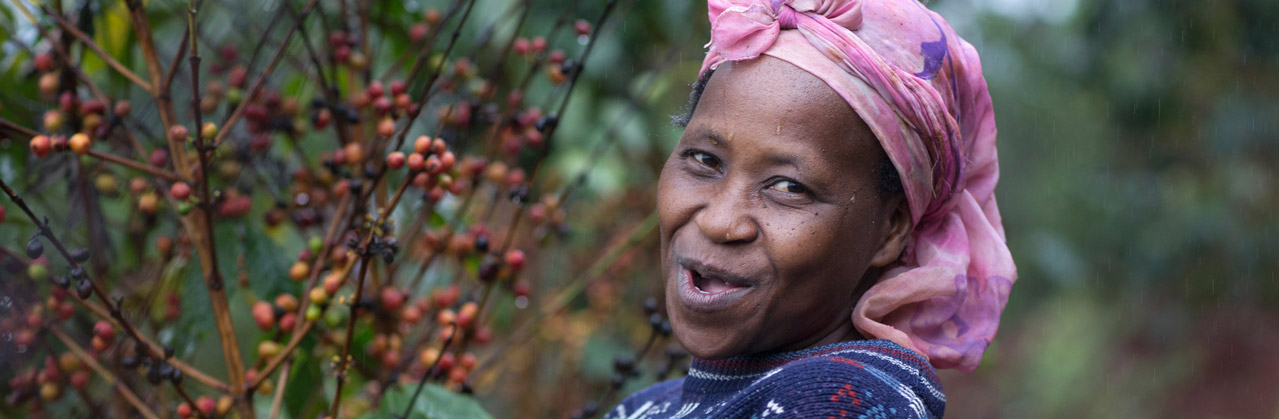
Six years ago, James Hoffman started a post on natural coffees saying, “You could say this debate is old news, but somehow it still seems to be rumbling on.”
Well, I’m fairly new to specialty coffee, and I’m so green to natural coffees that I was surprised (and delighted) to discover there was a debate. After studying and tasting natural coffees over the past several months, I decided to wade deep into this debate. My premise:
Naturals should play a big role in the future of specialty coffee for two reasons:
- Natural coffees have a far smaller water footprint than wet-milled coffees.
- Natural coffees taste fantastic.
What is natural coffee?
For those of you who are (also) new to natural coffee, no worries. The fact of the matter is that there are a lot of terms used to describe natural coffees: “pulped natural”, “honey coffee”, “dry-milled”, and “semi-washed” are just a few. And I find that experts are not always consistent in how they use these terms. (For a quick rundown on definitions, see the final section of this an article by Kenneth Davids in Coffee Review: “Honey and Pulped Natural Coffees”).
In a nutshell, “natural coffees” are those that have been dried with all or some of the fruity pulp (and sometimes skin) adhering to the bean. In contrast, the wet-mill process uses water to wash and ferment coffee beans to remove all the skin, pulp, and mucilage off the bean.
A recent article on “Understanding the Debate Over Natural Processed Versus Washed Coffees” by Ryan Ahn gives a great summary of the differences between wet-milled and natural coffees processing.
Natural-coffees use far less water than wet-milled coffees
What fascinates me about natural coffees is how little fresh water is required to process them. Whereas wet-milled coffee can use at least 10 liters (and sometimes much more) of water per kg of dry parchment, the natural process can use far less than 1 liter per kg. If you extrapolate that across many farms and mills in a landscape, the impact on water resources is dramatic. (My next post will deal with the water footprint of coffee, and what’s wrong with that metric).
Given that at least 85% of coffee mills around the world still do not use water-efficient practices and technologies – and very few coffee buyers and roasters help coffee producers invest in upgrades to their mills – I am very impressed with the natural alternative to wet mills.
The Debate.
The debate about natural coffees is a serious one, and a good one. No easy answers. Washed or un-washed? Natural or un-natural? When you dig in, there’s a lot of grey here.
Geoff Watts apparently has a great post on this on the Intelligentsia blog, but the original post is no longer online. His point was that “dry-processed coffees… are probably not the kind of coffee we want to promote”.
From what I can tell, the major issue is the inconsistency of quality of natural coffees versus wet-milled coffees. Geoff Watts makes the noble case that the “fanatical” demand for dry-milled coffees can put coffee farmers at risk when the (fickle) market turns against them.
These are great points, but the debate is alive and well. As water scarcity is becoming a major concern in many coffee producing countries, the debate is not trivial.
Natural coffees (can) taste great.
At Symposium 2015, Dr Flavio Borem gave a fascinating talk on the science of what happens in the natural drying process, making the case that natural coffees can be fantastic coffees if they are dried well.
Personally, I have tasted some excellent natural coffees. And I’ve found that quite a few professional cuppers and buyers share that view. Here are a few random excerpts of recent reviews online:
- “the fruit-like quality and full body of natural processed coffee can be very well balanced and harmonious, resulting in a delicious and easy-to-appreciate cup of coffee with its own subtleties and nuances.”
- “ … hint of brandyish fruit ferment overlaying a cherryish dark chocolate, suggested a quieter, more restrained version of fruity natural-processed coffees”
- “richly dry and tartly sweet, a structure we might expect from a wet-processed coffee, though the intense chocolate-toned richness I suspect derives from the deepening and rounding impact of the honey processing method.”
If your local coffee shop isn’t carrying a natural coffee option, you’re missing out.
The bottom line:
Based on what I’ve learned so far, I think that natural coffees should have a future, and that the coffee industry (from roasters to farmers) should invest in methods and systems to make natural coffees more consistent.
–Paul Hicks