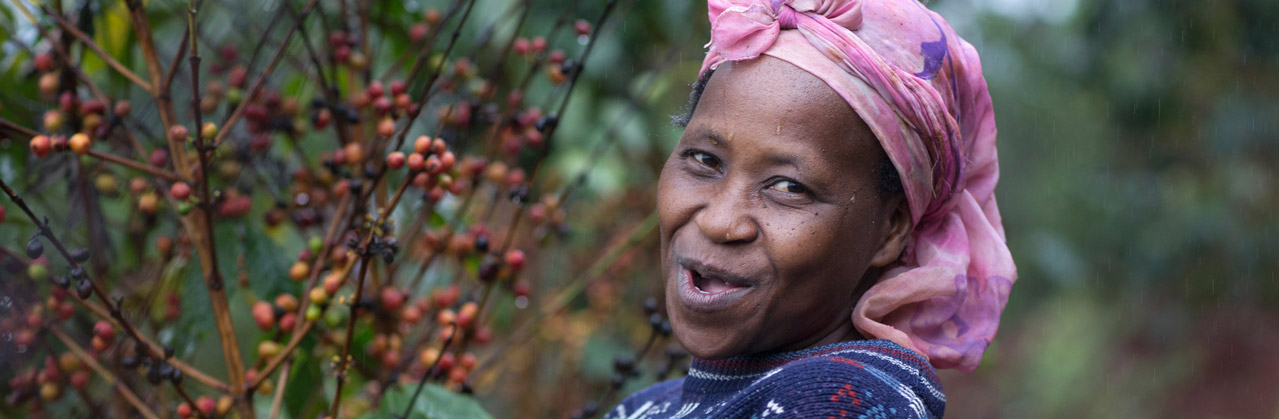
The drivers of migration remain the usual suspects: climate change, debt and prices, and, in some parts of the Northern Triangle, violence. But the pressure of these forces is increasing, and it is hard to ignore their compounding nature when you are dealing with them all at once. The hard numbers[1] as well as numerous qualitative features[2] seem to bare out the hypothesis that the pressure on Central America´s coffee farmers is growing.
For those who were following the news prior to the November midterm elections in the US, you probably came across the story of the migrant caravan a few times during your daily reading (another one left Honduras in January). Although these caravans are not uncommon, the size of the one in the fall caught some by surprise. What caught my field team by surprise, was that before the caravan, and right around the time the C-Price dropped below a $1/pound we started to hear from our staff about a slow exodus of program participants, family members, and friends or acquaintances in the region, making the journey North.[3] Our field team began to investigate what was driving these seemingly sudden decisions, and contribute to the growing press coverage of the issue. What we ascertained was threefold:
1. Complex decisions — Decisions to migrate are multi-year decisions. It’s not all about the price and it doesn’t happen overnight (this gets at the complexity of building a sustainable industry or value chain). Migrating to the US is expensive and dangerous. It entails leaving your loved ones behind and not knowing when you might see them again. There tends to be a compounding of factors (coffee leaf rust, drought, prices), which leads to a farmer taking this seemingly discrete decision (literature on the economics of migration seem to back up this assertion regarding the complexity of the decision-making process).[4]
2. Debt/Prices — Coffee farmers are carrying more debt than other farmers. Coffee farmers in CRS programs tend to be more dependent on

This Guatemalan coffee nursery represents a small part of the labor, cost and risk farmers face when deciding to invest in their coffee farms. Photo by Oscar Leiva/Silverlight for CRS
one source of income. For instance, our grain farmers often have well-developed internal migration networks and rely on non-agriculture income sources as well. This means that coffee farmers are more vulnerable to the ups and downs of production and market prices. Complicating matters, coffee farmers are heavily reliant on credit to make their operation work. They rely on credit (and some savings) for 8-9 months out of the year until payday during the coffee harvest. In a context where there is generally no insurance or sophisticated price risk management tools, farmers are thus in dire straits when prices drop over the course of the year, after they have already committed their harvest in exchange for a credit advance.
A farmer recently told us that when price signals reached him before the harvest, he knew he only had one option: migrate. He called the decision “re-capitalization.” He would go to the US to build up some capital, pay off debts, and maybe invest in his farm again. In an average year, our coffee farmers carry a debt-to-income ratio of about 50%. In recent years that number has climbed higher with the additional debt (and opportunity cost) of farm renovation.
To exemplify this growing problem, I spoke with a farmer named Fernando yesterday whose debt-to-income ratio had risen to 75%. He said he generally owes about half of his harvest to the intermediary who bankrolls him 9 months out of the year. However, due to the low price of coffee, he owes much more this year. He figures he will end up putting about $600 in his pocket after annual debts are taken care of. That will last his family till about April.

Coffee leaf rust hit Central American farmers hard in 2012-13, forcing many to consider the high cost of replanting, abandoning coffee altogether, or heading north to “recapitalize their farm operations. Photo by Oscar Leiva/Silverlight for CRS
3. Climate Shocks: Rust/Drought — The coffee leaf rust outbreak of 2012-13 decimated farms, leading to production drops of 20% across the region, and the loss of 100’s of millions of dollars of revenue (half a billion just in Guatemala).[5] There hasn’t been a severe outbreak since but given coffee´s perennial nature, farmers are still dealing with the consequences of the outbreak. Many farmers made a bet on coffee and began to renovate their farms from 2014-16. They were just seeing those plants come online last year and this year. There was optimism, but this price drop came at the worst possible time for farmers just returning to pre-2012 production levels. During the months of July and August 2018, farmers who were receiving early word of what prices would look like this harvest (November-February) feared they would be left once again in the red.
In my next post, I’ll dig into our project´s cost of production numbers to see what they look like at the farm level. I will do some analysis of the numbers and compare them to another tree crop (macadamia) using tools such as the Land Equivalency Ratio and gross margin analysis. Afterwards I will hypothesize about what they might mean for farmer profitability and decision-making.
[1] https://www.cbp.gov/newsroom/stats/usbp-sw-border-apprehensions
[2] 1) https://www.npr.org/2018/09/19/649300559/a-guatemalan-village-tells-the-story-of-immigration-to-the-u-s; 2) https://www.univision.com/especiales/noticias/2018/la-gran-industria-de-la-migracion-guatemalteca-migracion-de-guatemala-estados-unidos-coyote-cumplir-el-sueno-americano/; 3) https://www.nytimes.com/2018/10/07/world/americas/guatemala-immigration-usa-mexico-border.html
[3]Although the price has recovered a bit, as recently as last week, farmers in Zacapa and Chiquimula were still only receiving $0.75/lb for parchment at farmgate.
[4] Balaz, Vladimir & Williams, Allan. (2017). Migration decisions in the face of upheaval: An experimental approach. Population, Space and Place. 24. e2115. 10.1002/psp.2115.
[5] https://www.prensalibre.com/economia/impacto-de-la-roya-en-guatemala-perdidas-por-la-roya-y-la-exportacion-volumen-de-venta-caficultura-en-crisis/